Third Party Auditors performing Structural Soundness Evaluations and Architectural Integrity Assessments or Audits of building projects help to point out major or minor lacunae and optimize the project in all aspects.


Imagine moving into the home you have worked hard to buy and finding major snags like swollen floor tiles, cracks in structural members or faulty electrical wiring? Customers who went through one such harrowing experience raised complaints against their developer. As it turns out, there were major construction quality and design problems which went unidentified as no third party structural audit or design review had been carried out for the building. A worst-case scenario played out where the snags were so drastic that the developer had to demolish the building and rebuild it as per norms and codes resulting in project costs that ran into more than hundred crore Rupees.
Cases such as these highlight the importance of Structural Design Audits and Architectural Design Reviews of buildings to ascertain their adequacy and reduce human errors in all the aspects of design and construction.
Stages of Design
There are several stages in the lifecycle of a building project.
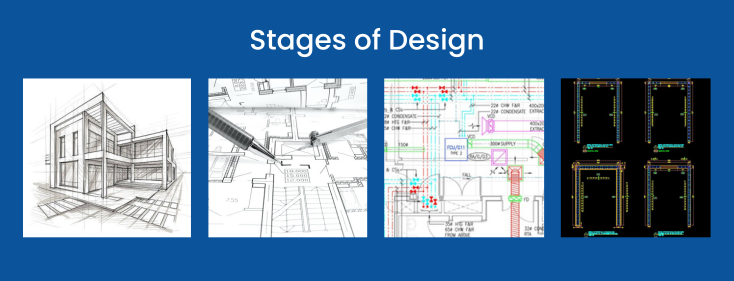
- Concept Drawing Stage (CD) – This is where the Architects and their team ideate on the built form and function and come up with concept drawings. Building aesthetics, planning and placement of services, people and goods circulation, approaches from roads, building elevations and design, materials etc are the Architect’s prerogative.
- Schematic Drawings Stage (SD) – SD is the next stage when the team has a rough idea of the building design and the structural designers check the CD as per the structural requirements like beam and column sizes and codes like Indian Standard (IS) codes and ISO standards. There can be numerous iterations in the design at this stage as the design goes to and fro from the CD to the SD stage.
- Design Drawing Stage (DD)– Once the design is frozen upon, the next stage is making Design Drawings (DD) which involves optimizing the structural design of the project by the structural designers.
- Good For Construction (GFC) – Good For Construction (GFC) is the final step where the design is ready for execution on site and the data is handed over to the client.
When are Audits done?
In a certain residential building, the architect designed 12 feet long, grand cantilever balconies and the design was vetted by the structural designer too for stability. It was all set to be executed when the Structural Auditor pointed out a clause in the building codes that states that in case of such a large cantilevers, the building must be designed for 5 times the earthquake resistance. Following this code meant that the cost of construction per floor went up by 1.2 times and from the developers point, an increase in the cost was completely undesirable. Hence the balcony cantilever was changed from 12 to 5 feet resulting in a structure that was built as per safety standards and saving costs.
- Ideally, third party Structural Auditors and Reviewers should be involved at the Concept Drawing stage as there can be some lacunae that even the project team’s structural designers may have overlooked as illustrated.
- The role of a Structural Designer is making the building structurally safe for use by ascertaining the quality of concrete and other materials, the grade of steel, providing an economical design in order to optimize the project and address the specific demands of the architect. However, certain aspects can go unnoticed by them and this is where third party auditor’s role comes in – to reduce the human errors made in the course of the project design.
- Auditors involved right from the CD stage see to it that the checkpoints are followed from the start of the project and whether services like Mechanical, Electrical and Plumbing (MEP) are working out in the architect’s design.
- Auditors can also help in certain aspects of design and give recommendations, for example if the architect wants large spans in the design, auditors can suggest methods like post tensioned or voided slabs.
- Practically, what happens in the field is that Structural Audits and Reviews are usually done at the Schematic Drawing stage.
Audits at an Advanced Stage in Construction
- Auditors had suggested a different execution method for a project that had already reached the Design Drawing stage. For instance in a G+13 building, a fast construction way called the Tunnel formwork method was recommended over conventional construction method. That would mean the project would be completed in just a year as against 3-4 years.
- Our experts say that a lot also depends on the acceptance of the proposals by the client. Changes means overhauling a lot of aspects and sometimes clients are just looking at rectifying certain errors by way of audits.
- At the DD stage Auditors recommend alterations in order for the design to adhere to the building codes and standard and also point out issues like sizes of structural members, casting issues of members, cost optimization by various methods and so on.
- When Auditors are roped in after GFC, their job is much more difficult as their suggestions are usually met with a lot of resistance. If their changes are not incorporated then the project cannot be issued a Stability Certificate.
Stability Certificate

Only agencies with the requisite experience in structural design and professionals can issue Stability Certificates. Traditional designers generally follow conventional methods and use rule of thumb that end up increasing project costs. Blunders on site can cause major problems and thus experienced persons like auditors are needed to manage the quality and safety checkpoints in building projects.




